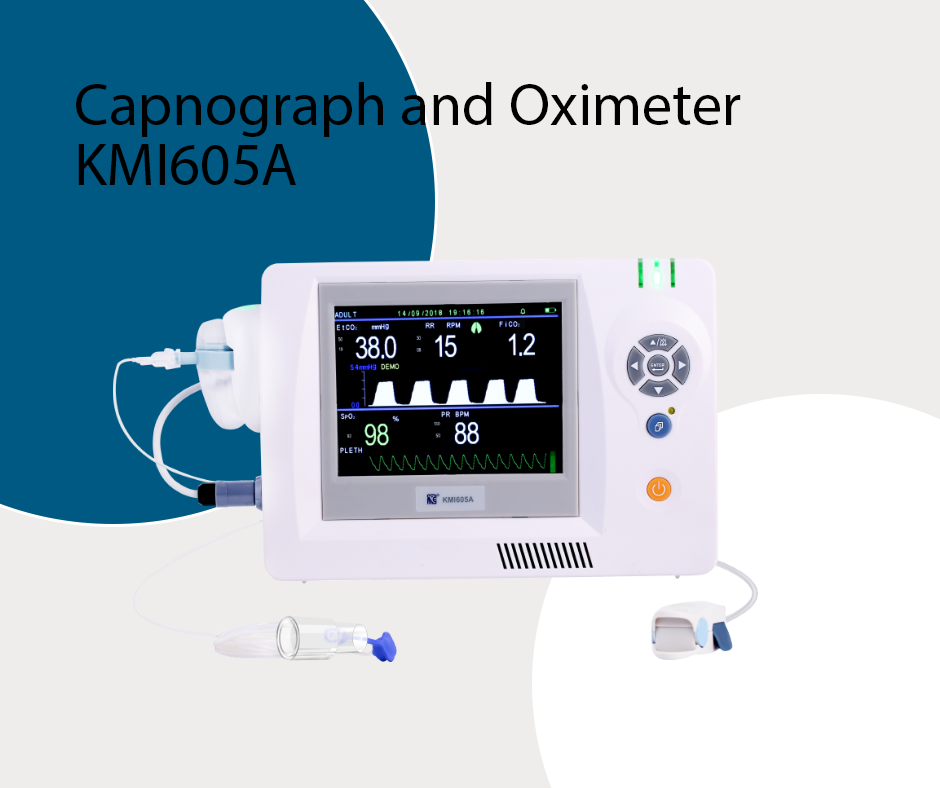
In the field of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency medicine, the monitoring of end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2) is an extremely important tool used to assess cardiopulmonary function, guide emergency measures, and provide information about patient prognosis. Here is a detailed explanation of ETCO2 in cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency medicine:
1. Assessment of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Quality:
ETCO2 monitoring can provide real-time feedback on the quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. During cardiopulmonary resuscitation, effective chest compressions can increase cardiac output, promote tissue perfusion, and thus elevate ETCO2 levels. Therefore, monitoring ETCO2 levels can be used as one of the indicators to assess the quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
According to international resuscitation guidelines, monitoring ETCO2 levels is recommended as an indicator of the quality of chest compressions during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Achieving a certain level of ETCO2 can be considered a marker of effective cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
2. Guidance for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Measures:
ETCO2 monitoring can provide guidance for healthcare providers to adjust cardiopulmonary resuscitation measures. For example, during cardiopulmonary resuscitation, healthcare providers can adjust the frequency and depth of chest compressions based on ETCO2 levels to achieve more effective cardiac output.
Additionally, ETCO2 monitoring can also be used to guide adjustments in ventilation parameters. Adequate ventilation support during cardiopulmonary resuscitation can facilitate gas exchange and carbon dioxide elimination, thereby increasing ETCO2 levels.
3. Prediction of Patient Prognosis:
Several studies have shown that ETCO2 levels in cardiac arrest patients are closely related to patient prognosis. Higher ETCO2 levels are usually associated with better outcomes, as they reflect better cardiac output and tissue perfusion. Therefore, ETCO2 monitoring can be used as an indicator to predict patient prognosis during cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
ETCO2 levels below a certain threshold may indicate a poorer prognosis, which may require more aggressive treatment measures or consideration of discontinuing cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Documentation:
ETCO2 monitoring can provide continuous monitoring and documentation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Healthcare providers can assess treatment effectiveness by monitoring changes in ETCO2 levels and adjust treatment measures promptly.
Furthermore, ETCO2 monitoring can also provide real-time information about patient cardiac function and circulatory status, helping healthcare providers make timely clinical decisions.
In summary, ETCO2 monitoring plays a crucial role in cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency medicine. It can be used to assess the quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, guide emergency measures, and provide information about patient prognosis, thereby improving the effectiveness of emergency treatment and patient survival rates.