Monitoring end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO₂) in veterinary medicine is becoming increasingly important, particularly in anesthesia management, respiratory disease monitoring, and emergency care. As a non-invasive, real-time respiratory monitoring parameter, ETCO₂ helps veterinarians assess pet respiration more accurately, improving treatment outcomes.
During pet surgeries, general anesthesia can suppress spontaneous breathing, leading to hypoventilation or hyperventilation. Continuous ETCO₂ monitoring allows veterinarians to:
Evaluate ventilation and prevent CO₂ retention or hypocapnia.
Detect incorrect endotracheal tube placement, avoiding esophageal intubation.
Adjust ventilator settings to ensure proper ventilation support.
Identify potential anesthesia complications such as alveolar hypoventilation or respiratory depression due to anesthetic overdose.
Assess ventilation adequacy during non-invasive sedation or anesthesia.

For pets suffering from respiratory conditions such as asthma, pulmonary edema, chronic bronchitis, or lung infections, ETCO₂ monitoring can:
Reflect airway resistance and ventilation efficiency, aiding in severity assessment.
Track improvements during treatment, optimizing therapeutic approaches.
Serve as a non-invasive screening tool, reducing pet stress.
Identify early risks of respiratory failure, preventing treatment delays.
Provide continuous data support for long-term oxygen therapy or ventilation strategies.
ETCO₂ monitoring is essential in veterinary emergency and critical care. For example:
During cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), ETCO₂ serves as a key indicator of resuscitation effectiveness and prognosis.
If ETCO₂ remains below 10-15 mmHg, the likelihood of successful resuscitation is low.
A sudden rise in ETCO₂ may indicate the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC).
For pets experiencing respiratory failure or hypovolemic shock, ETCO₂ variations assist in treatment adjustments.
In post-surgical recovery, ETCO₂ monitoring helps detect potential respiratory complications such as airway obstruction or atelectasis.
In severe trauma, sepsis, or shock cases, ETCO₂ helps evaluate tissue perfusion status.
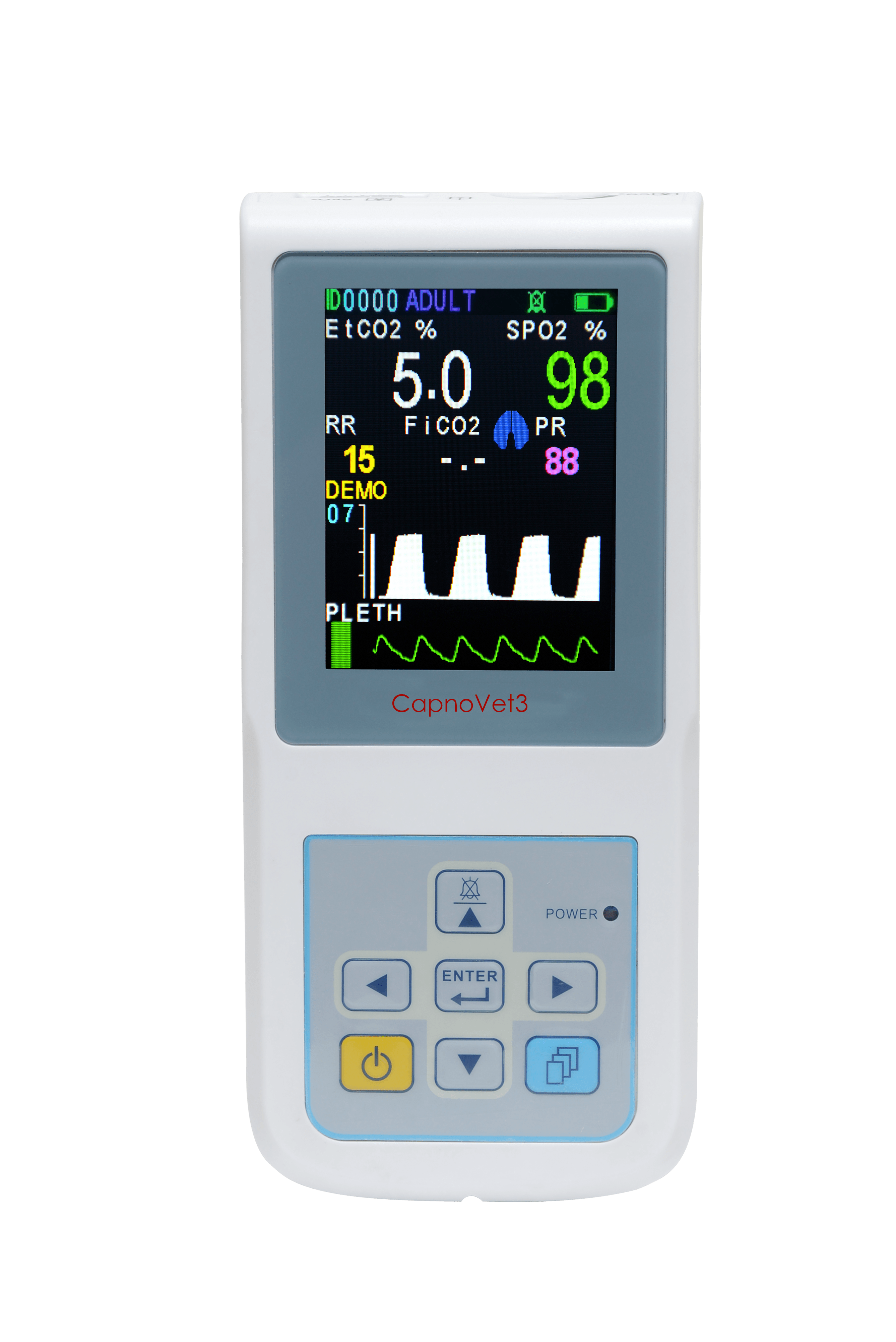
With advancements in veterinary monitoring equipment, portable ETCO₂ monitors have become more widely available, allowing veterinarians to utilize this technology in surgical, critical care, and even home settings. Some innovative pet ETCO₂ monitors feature non-intubation designs, enhancing pet comfort and expanding usability.
Common ETCO₂ monitoring devices in the market include:
Mainstream ETCO₂ Monitors: Directly connected to an endotracheal tube or mask, providing rapid real-time data.
Sidestream ETCO₂ Monitors: Suitable for non-intubated pets, using nasal cannulas or masks for sampling—ideal for post-surgical monitoring or general respiratory assessment.
Portable ETCO₂ Monitors: Designed for veterinary emergency care, home monitoring, or wildlife research, offering flexible monitoring solutions.
Although ETCO₂ monitoring is widely used in veterinary medicine, several challenges remain:
Adaptability across different animal species: Anatomical differences in the airways of cats, dogs, rabbits, and other animals require device optimization.
Sampling method limitations: Small pets or animals intolerant of masks may affect sample quality.
Environmental influences: Oxygen concentration in open environments and pet movement can impact measurement accuracy.
Future advancements in ETCO₂ monitoring may include:
Miniaturized, wireless devices for improved clinical use and mobile monitoring.
Higher precision sensors to reduce sampling errors and improve reliability.
Integration with artificial intelligence, enabling automatic detection of abnormal breathing patterns and assisting veterinary diagnosis.
ETCO₂ monitoring provides precise, real-time respiratory assessment in veterinary medicine, playing a crucial role in anesthesia, respiratory disease management, and emergency care. With continuous innovation and widespread adoption of veterinary equipment, this technology will further enhance pet healthcare quality.
If you are a veterinarian or pet care professional, consider incorporating ETCO₂ monitoring into your clinical practice to offer safer and more effective treatment options!
